Why do you need Omega 3 fatty acids in your food and why are they different to any fats we have in our food?
Omega 3 fatty acids make up a very small proportion of the fats that we eat (250 – 500mg), but they function very differently to other fats that we eat.
They are not really used as energy, but affect the actions of eicosanoids, a signalling molecule in your tissues that effect important functions such as inflammation and blood clotting.
The diagram below, details this eicosanoid pathway:
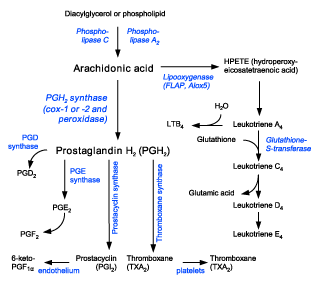
The direction this pathway takes is dependent on the balance between Omega 6 and Omega 3 fatty acids that we eat in our diet.
As we can not convert Omega 6 fats into Omega 3 fats and vice versa, it is completely dependant on what we eat. Both elements are important for our normal function, but when the balance is screwed in one direction (almost exclusively towards Omega 6’s), this increases the amount of blood clotting and inflammatory signalling molecules we have in the body.
As our proportion of Omega 3’s increases, these have the following effect:
- Reduce the amount of inflammatory signalling molecules
- Reduce blood clotting
- Reduce blood pressure, due to the reduced inflammatory signalling molecules
- Reduce heart arrhythmias
Although the results are quite variable, in general the recommended doses to be effective are:
- 1g of Fish oil ( which contain about 300mg of direct omega 3 fatty acids) for heart health
- 3g of Fish oil ( which contain about 900mg of direct omega 3 fatty acids) to have an anti-inflammatory effect
Want to know more?
If you want more information or would like to book for a FREE full body assessment with one of our Physiotherapists or Exercise Physiologists, call us on 9857 0644 or email us at admin@md-health.websitepro.hosting



