Acromio-Clavicular (AC) Joint Injury - Fact Sheet
What is a Acromio-Clavicular (AC) Joint Injury ?
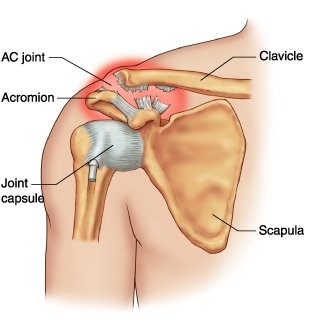
An AC joint sprain is a relatively common sporting injury affecting the shoulder and is characterized by tearing of the ligaments or disruption of the joint surfaces of the Acromio-Clavicular joint (AC Joint). The AC joint is responsible for connecting the shoulder blade with the clavicle (collarbone) and is the main point of articulation of the shoulder on the bodies’ trunk.
What causes it?
An AC joint sprain can occur from direct contact or trauma to the shoulder. This commonly occurs in contact sports due to a collision with another player, but may occur following a fall onto the point of the shoulder.
Signs and Symptoms of Acromio-Clavicular (AC) Joint Injury?
• Pain at the tip of the shoulder, usually sharp, particularly with overhead movements.
• Depending on the severity of injury, a step deformity may be present – where the collarbone and acromion bones are slightly separate of each other, indicating ligament tearing
• Pain with lying on the affected side, with heavy lifting, pushing or pulling movements
Diagnosis of an Acromio-Clavicular Joint Injury:
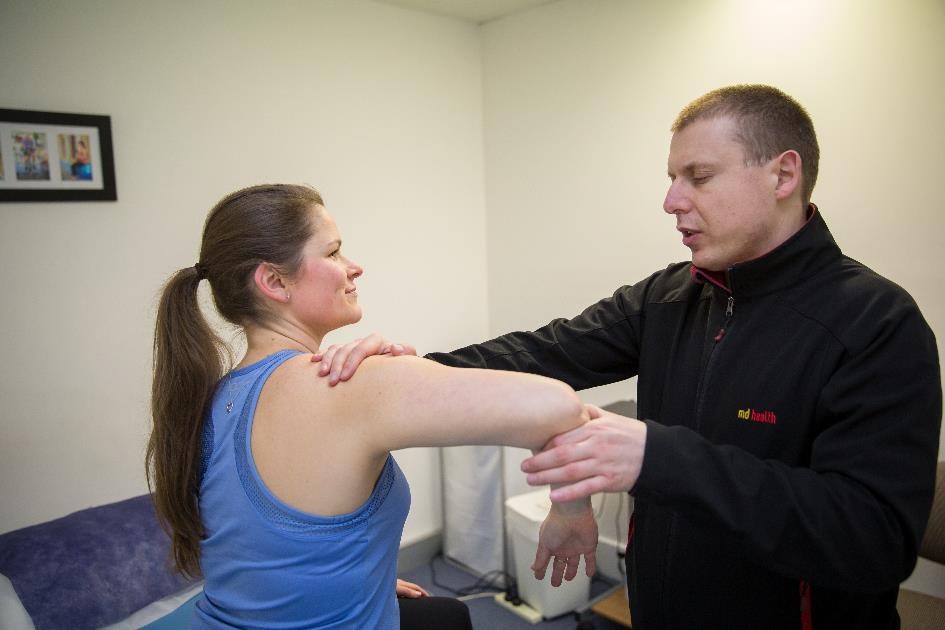
An assessment from a MD Health Physiotherapist, Accredited Exercise Physiologist or Osteopath is usually enough to diagnose an AC joint sprain. Investigations such as an X-Ray or MRI may be indicated to determine the extent of injury, or to exclude the possibility of a fracture.
.
Treatment of AC Joint injury ?
Most patients with an AC joint injury heal well with appropriate exercise-based rehabilitation. Depending on the severity, rest from sport and wearing a sling is sometimes indicated.
Treatment may include the following:
• Acute injury management – Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation – used to minimize the pain and swelling.
• Restore pain free range of motion, and strength+++
• Modified training – avoidance of aggravating activities, followed by a slow re-introduction to these movements
• Return to full training &/OR activity (generally takes around 2-8 weeks).
Ignoring symptoms or adopting a ‘no pain, no gain’ attitude is likely to lead to the AC joint sprain becoming chronic. Immediate, appropriate treatment in patients with an AC joint sprain is essential to ensure a speedy recovery.
Other intervention for an AC joint sprain
Despite appropriate conservative management, a small percentage of patients with an AC joint sprain may not improve adequately. When this occurs, the treating physiotherapist can advise on the best course of management. This may involve pharmaceutical intervention, corticosteroid injection, further investigation such as an X-ray, CT scan or MRI, or a review by a specialist surgeon who can advise on any procedures that may be appropriate to improve the AC joint sprain.