Knee Osteoarthritis - Fact Sheet
What is a Knee Osteoarthritis ?
.
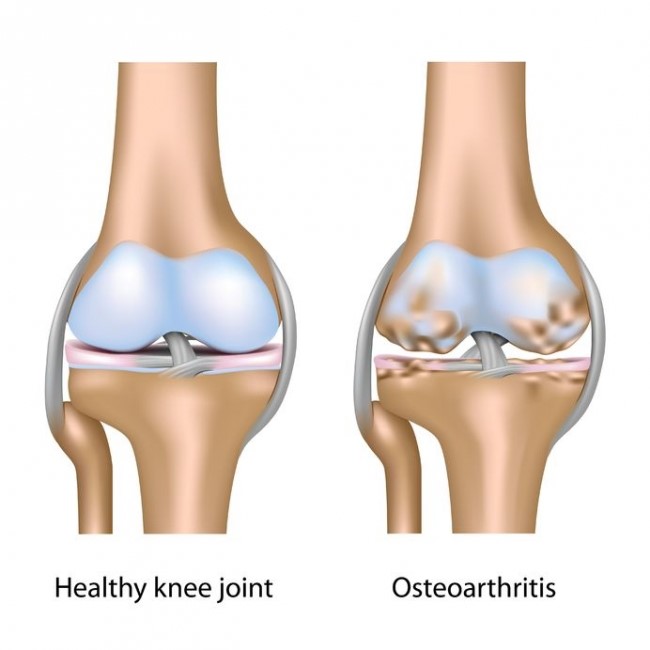
Signs and symptoms knee osteoarthritis?
- Pain around the knee joint or shin
- Pain after long walks, or after standing for a long duration
- Joint stiffness, usually in the morning
- Pinching type pain with particular movements, sometimes associated with sharp “locking”-type pain
- Pain is usually intermittent, off/on pain, of varying severity
- Pain with activities involving loading the knees, such as walking uphill or climbing stairs.
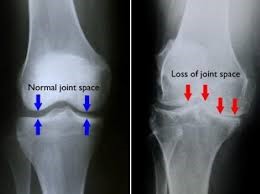
- Noticeable loss of joint space between the femur and tibia, on X-Ray
Treatment of knee osteoarthritis ?
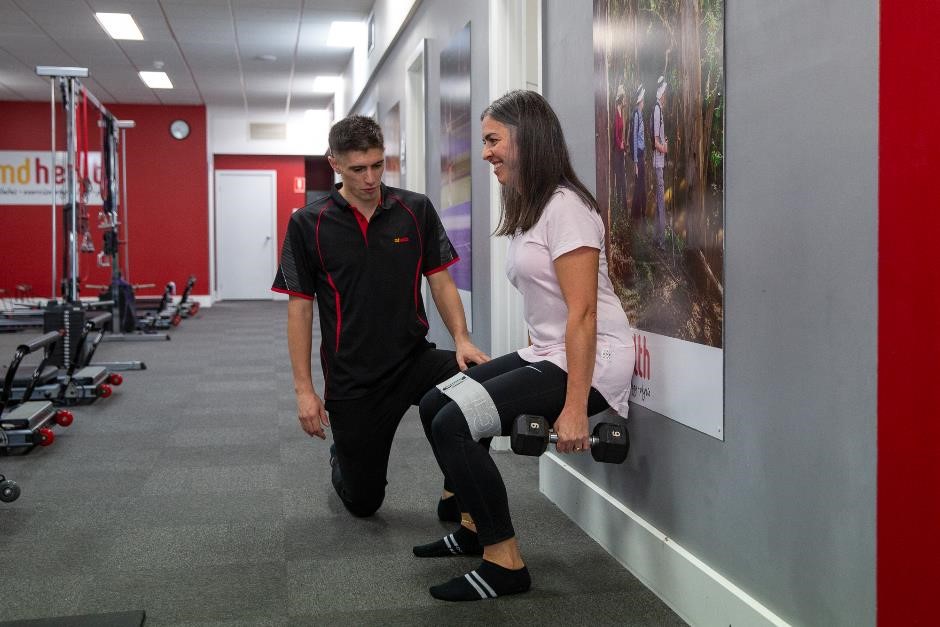
Tailored Clinical Exercise – will help to strengthen the muscles that support your knees (including your quadriceps, hamstrings, calves, as well as hip stabilisers and rotators), thus decreasing the severity and re-occurrence of your knee pain. Osteoarthritis in general is an irreversible condition BUT building muscle bulk and strength around the affected joints can help reduce the symptoms of OA.
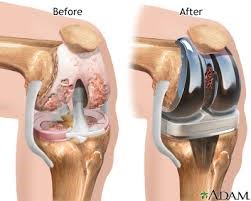
Referral – If the Knee OA pain is unrelenting, or the joint degeneration is severe enough, referral to an orthopaedic surgeon may be indicated, for a potential Total Knee Replacement.
Other things to be aware of:
Flare ups – Re-occurrences of osteoarthritic pain often occur, but it is important to remember that this is a normal pain behaviour for the condition. Complete rest (such as bed rest) is NEVER the answer – keep moving, keep positive – your symptoms will eventually settle down.
Take medication – During acute flare ups, painkillers and anti-inflammatories can help control the severity of your symptoms. Ask your doctor or pharmacist what medication is right for you and be aware of possible side effects. In severe cases, medication can control the pain so that physical activity can begin.
.