Cervical Headache - Fact Sheet
What is a Cervical Headache ?
What causes it?
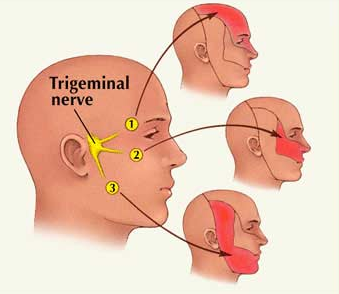
Irritation of the facet joints can lead to some sensitivity of the exiting nerve roots of the upper cervical spine. These nerve roots give rise to a nerve called the Trigeminal nerve, which distributes feeling and sensation to areas of the face and head.
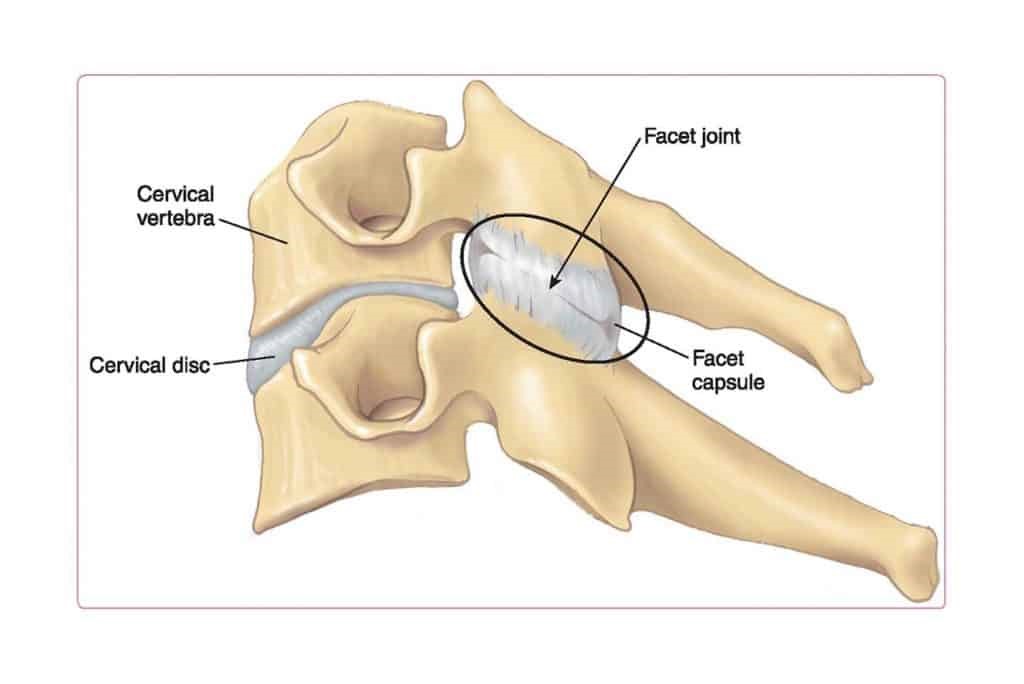
Signs and Symptoms of Cervical Headaches ?
• Neck stiffness, particularly looking upwards and rotating the neck
• Headache in 1 or more of these three areas: Suboccipital (base of the neck and skull), Temporal (side of the head, moving towards jaw) or Frontal (front of the head, the eyes, occasionally into the cheeks).
.
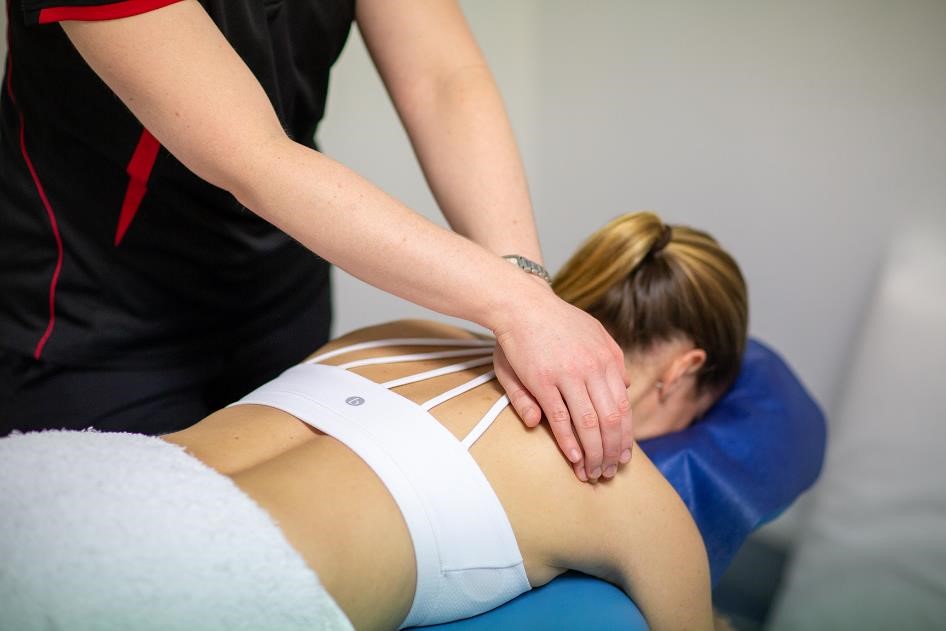
Treatment of Cervical Headaches ?
Hands-on-treatment: mobilisation of facet joints in the upper neck, to reduce irritation of the nerves and reduce severity of symptoms. Upper cervical traction to take pressure off the facet joints. This should not be solely relied upon, as evidence suggests this works mainly in the short term, giving 2-3days relief.
Exercise: Neck-specific exercises to help relax bracing neck muscles, and to get the correct stabilising muscles of the neck switching on. Exercise for the muscles in the upper back (postural muscles) which also helps take pressure off the neck and set your head and shoulders into a more stable position.
***After treatment for Cervical Headaches, symptoms may get worse that evening, but generally improve the following day.
Red Flags of Cervical Headaches ?
Please let a health professional know immediately if you have any of the following symptoms:
- Random onset of particularly severe headache, with associated nausea, forgetfulness/confusion or difficulty speaking (which you have never experienced before)
- Headache associated with flu-like symptoms (fever etc.)
- Headache with severe onset following coughing or sneezing
- New headache with individual history or family history of aneurysm
- New headache with individual history or family history of cancer
This is an indicator that further medical testing may be useful in order to rule out any more severe causes of headache.



