Elbow Pronator Teres tendinopathy (Golfer’s elbow) - Fact Sheet
What is elbow pronator teres tendinopathy (Golfer’s elbow)?
Elbow Pronator Teres Tendinopathy, or commonly referred to as “Golfer’s Elbow” because it is a common injury in golfers, as well as other athletes who perform repetitive motions that involve the forearm muscles and tendons that attach to the medial epicondyle of the humerus, specifically the pronator teres muscle. The pronator teres muscle is responsible for rotating the forearm so that the palm faces downwards. The condition is caused by the repetitive gripping and swinging motions involved in the golf swing, which can place a significant amount of stress on the pronator teres muscle. However, it is not limited to golfers and can occur in anyone who performs repetitive activities that involve the forearm muscles and tendons, such as tennis players, carpenters, and painters.
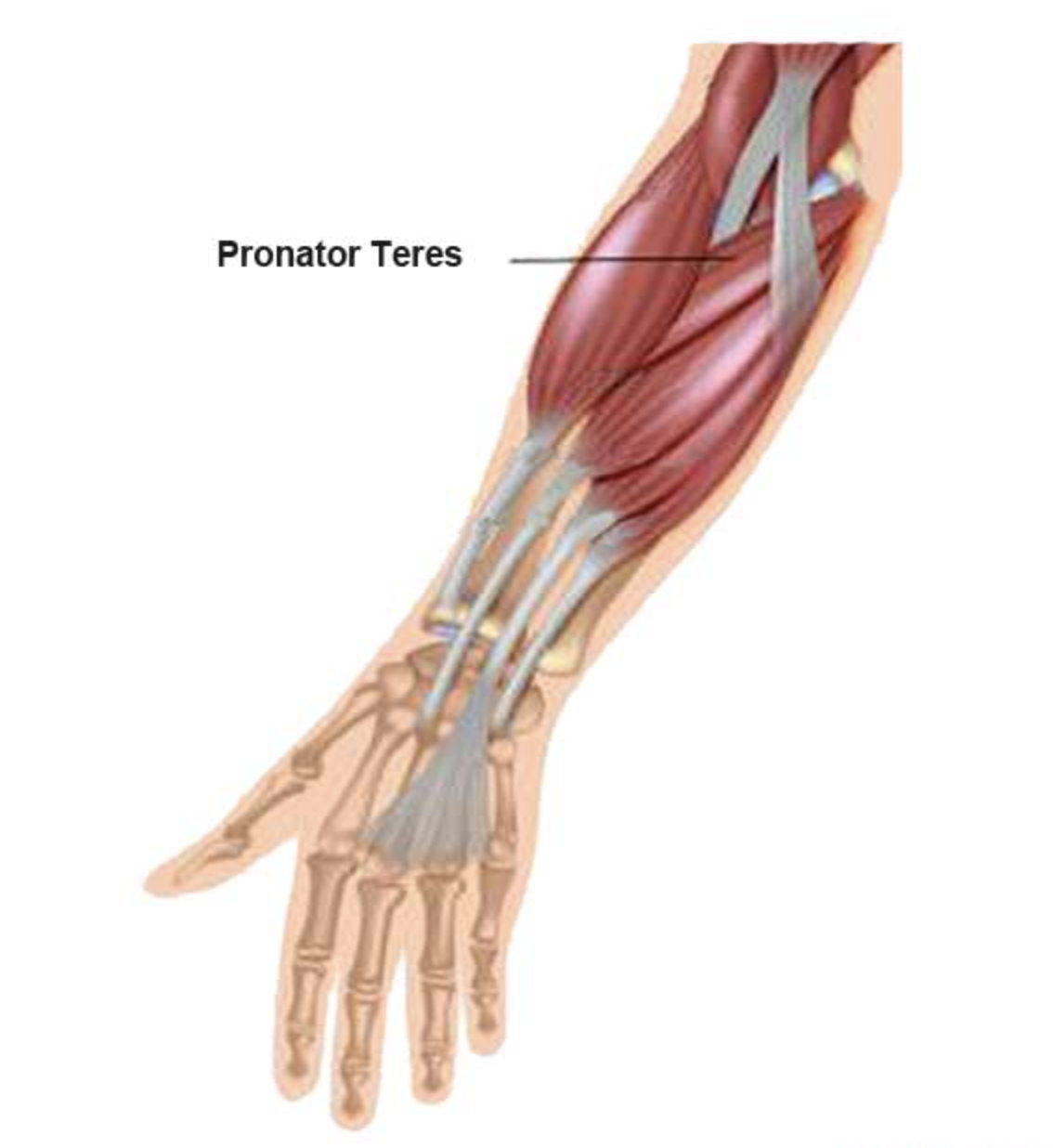
What causes Elbow Pronator Teres tendinopathy (Golfer’s elbow)?
Golfer’s Elbow is caused by overuse or repetitive stress of the pronator teres muscle and its tendons, which can result in inflammation and pain on the inside of the elbow. Repetitive gripping, twisting, or lifting activities, poor technique, using equipment that is too heavy or not properly fitted, and performing activities for extended periods without taking breaks are common risk factors. An acute injury, such as a direct blow to the inside of the elbow, can also cause the condition.

Signs and Symptoms
• Pain and tenderness on the inside of the elbow
• Weakness in the affected arm
• Stiffness in the elbow joint
• Difficulty making a fist or gripping objects
• Pain that worsens with gripping or twisting activities
• Radiating pain down the forearm
• Swelling and redness around the affected area (in some cases)
Symptoms that may appear gradually over time or suddenly after an acute injury. If left untreated, Golfer’s Elbow can lead to chronic pain and disability.
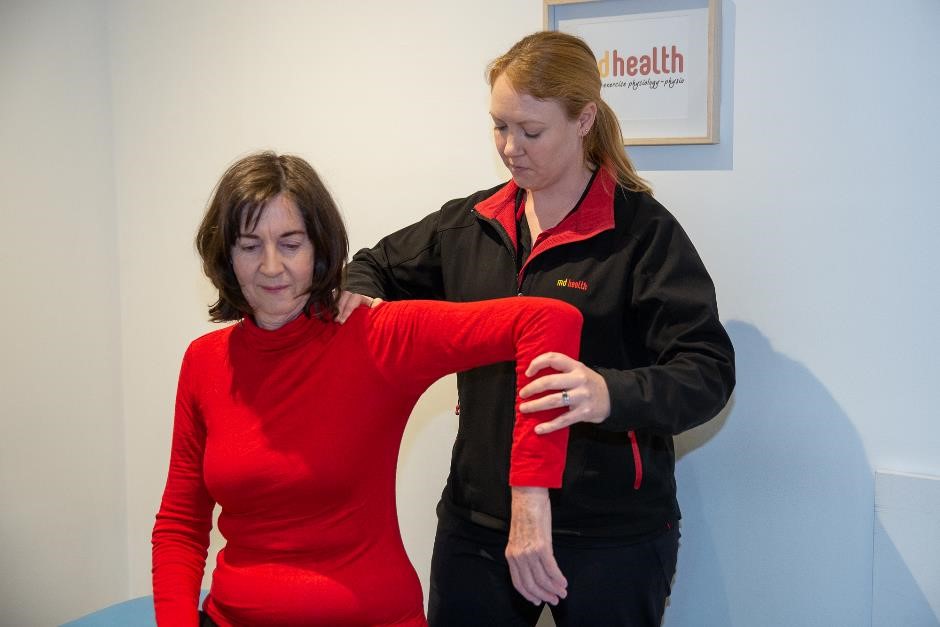
Treatment of Elbow Pronator Teres tendinopathy (Golfer’s elbow)?
Eccentric exercises – are designed to strengthen the affected muscles and tendons by lengthening them under tension. This type of exercise has been shown to be effective in treating Golfer’s Elbow.
Manual therapy – Manual therapy techniques, such as massage, joint mobilization, and stretching, can help to relieve pain and stiffness in the affected area, while also promoting healing.
Ergonomic assessment – A physiotherapist can assess the way you perform certain activities, such as gripping or lifting, and provide advice on how to modify your technique to reduce stress on the affected area. This can help to prevent future episodes of Golfer’s Elbow.