Hip instability - Fact Sheet
What is a Hip Instability ?
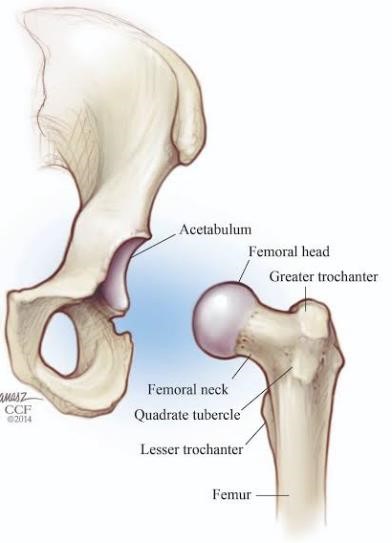
The hip joint is made up of the femoral head (a ball shape) and the acetabulum (the joint’s socket). This joint is deepened by a labrum (a sort-of joint covering) and stabilised with numerous ligaments.
Hip instability occurs when there is uncontrolled gliding of the hip joint during movement, which puts pressure on the supporting structures of the hip, causing irritation and pain.
What causes it?
Hip instability generally occurs in people who are naturally hypermobile in their joints, people who have history of an acute hip injury (such as dislocation or labral tear), or people who have difficulty engaging their deep hip stabilising muscles (including the quadratus femoris and gluteus minimus muscles).
Signs and Symptoms of Hip Instability ?
• Anterior hip pain, mostly with certain movements such as bending, or twisting on the hips
• Groin pain
• Clicking hips, with the click being felt at the anterior hip
• Periods of anterior hip irritation, particularly if the joint has been stressed repetitively (e.g. doing repeated squats)
• Poor lifting technique and hip control with movements such as squats
• Prolonged sitting
.
.

Treatment of Hip Instability ?
Activity modification – avoid or modify activities that flare up your hip pain – change the height of your seat at work, avoid deep squatting at the gym, or use a mirror for feedback to ensure your hips are remaining steady through this movement. This will ensure that you keep any hip pain at bay whilst you strengthen up the stabilising muscles of the hips!
Tailored Clinical Exercise will help to strengthen the deep gluteal muscles which help provide a suction effect on the hip joint. This improves the glide of the femoral head (the ball) in the acetabulum (the socket), reducing any pressure on the other sensitive structures of the hip. This is the best line of treatment for hip instability and can take a few months to fully reduce any pain associated with hip instability!
Referral – if your hip pain from instability does not subside in 3 or more months of clinical exercise, referral to a specialist hip surgeon may be indicated. Unsuccessful conservative treatment via exercise can indicate a hip labral tear or interruption, or a rupture of the ligamentum teres of the hip socket.



