Ulnar Collateral Ligament Injury (UCL injury) - Fact Sheet
What is ulnar collateral ligament injury (UCL injury)?
The ulnar collateral ligament (UCL) is a band of tissue located on the inside of the elbow joint that connects the ulna bone to the humerus bone. UCL injuries typically occur in athletes who throw overhead, such as baseball pitchers, javelin throwers, and tennis players, due to the repetitive stress exerted on the elbow joint during these activities. UCL injuries can range from a mild sprain to a complete tear of the ligament.
.
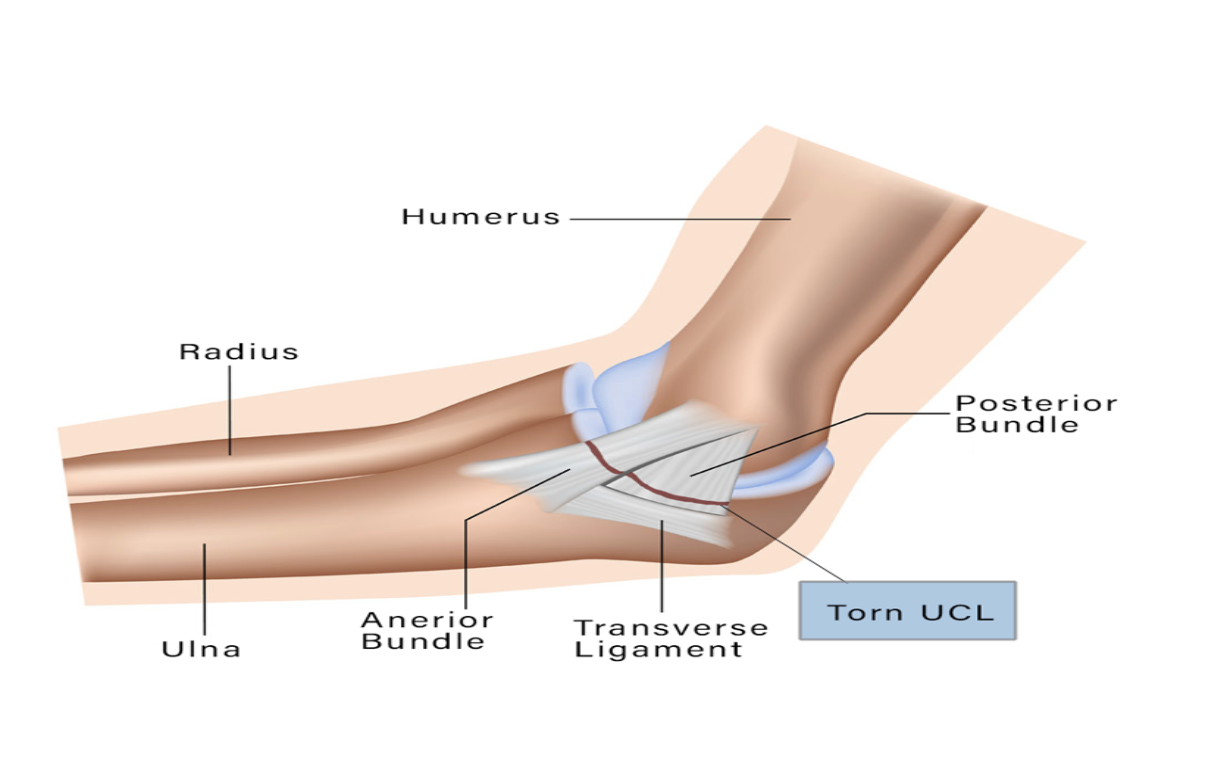
What causes Ulnar Collateral Ligament Injury (UCL injury)?
The ulnar collateral ligament (UCL) is an important stabilizing structure of the elbow joint, particularly during overhead throwing motions. UCL injuries are common among athletes who engage in throwing sports, such as baseball, softball, and javelin throwing. Repetitive stress from these activities can cause small tears or fraying of the ligament, which can eventually lead to a complete tear or rupture. While traumatic events can also cause UCL injuries, the majority of cases are related to the repeated stresses of overhead throwing.

Signs and Symptoms of Ulnar Collateral Ligament Injury (UCL injury)
•Abrupt “pop” or pain along the inner elbow, stopping the athlete from continuing to throw.
•Swelling and tenderness around the inner elbow.
•Decreased range of motion and strength in the affected arm.
•Swelling and tenderness around the inner elbow.
•Numbness or tingling in the fingers, indicating possible nerve involvement.
It’s important to note that the severity and combination of these symptoms may vary depending on the extent of the UCL injury. It’s always recommended to seek advise from your physiotherapist if you suspect a UCL injury, as early diagnosis and treatment can lead to better outcomes.
Treatment of Ulnar Collateral Ligament Injury (UCL injury)?
Range of motion exercises – these exercises aim to restore the normal range of motion of the elbow joint and prevent stiffness. Examples of range of motion exercises include wrist flexion and extension, elbow flexion and extension, and pronation and supination of the forearm.
Strengthening exercises – these exercises focus on strengthening the muscles that support the elbow joint, including the forearm, upper arm, and shoulder muscles. Examples of strengthening exercises include wrist curls, bicep curls, and tricep extensions.
Taping or bracing – Taping or bracing of the elbow joint may be used to provide support and stability, and to prevent further injury.
Functional training – This involves specific exercises that mimic the athlete’s sport-specific movements and gradually progress the intensity and volume of the activity. This can help the athlete regain their strength and range of motion and safely return to their sport.
It’s important to note that the specific physiotherapy treatment plan will depend on the individual athlete’s needs and the extent of their injury. A physiotherapist or sports medicine specialist can create a customized treatment plan that is tailored to the athlete’s goals and needs.